分表分库组件
大约 9 分钟
背景
为什么要自研
维护性;市面的路由组件比如 shardingsphere 但过于庞大,还需要随着版本做一些升级。而我们需要更少的维护成本。
扩展性;结合自身的业务需求,我们的路由组件可以分库分表、自定义路由协议,扫描指定库表数据等各类方式。研发扩展性好,简单易用。
安全性;自研的组件更好的控制了安全问题,不会因为一些额外引入的jar包,造成安全风险。 当然,我们的组件主要是为了更好的适应目前系统的诉求,所以使用自研的方式处理。就像shardingsphere 的市场占有率也不是 100% 那么肯定还有很多公司在自研,甚至各个大厂也都自研一整套分布式服务,来让自己的系统更稳定的运行。分库分表基本是单表200万,才分。
我们分库分表用的非常熟。但不能为了等到系统到了200万数据,才拆。那么工作量会非常大
我们的做法是,因为有成熟方案,所以前期就分库分表了。但,为了解释服务器空间。所以把分库分表的库,用服务器虚拟出来机器安装。这样即不过多的占用服务器资源,也方便后续数据量真的上来了,好拆分。
同时,抽奖系统,是瞬时峰值较高的系统,历史数据不一定多。所以我们希望,用户可以快速的检索到个人数据,做最优响应。因为大家都知道,抽奖这东西,push发完,基本就1~3分钟结束,10分钟人都没了。所以我们这也是做了分库分表的理由。
实现思路
- 借助mybatis提供插件特性,对执行的sql进行拦截,按预定的配置,进行sql拼接,做到指定表指定库的操作。
- 如何让入库的数据散列得更加均匀,这里借鉴了HashMap 底层散列原理 改进实现。
原理架构图
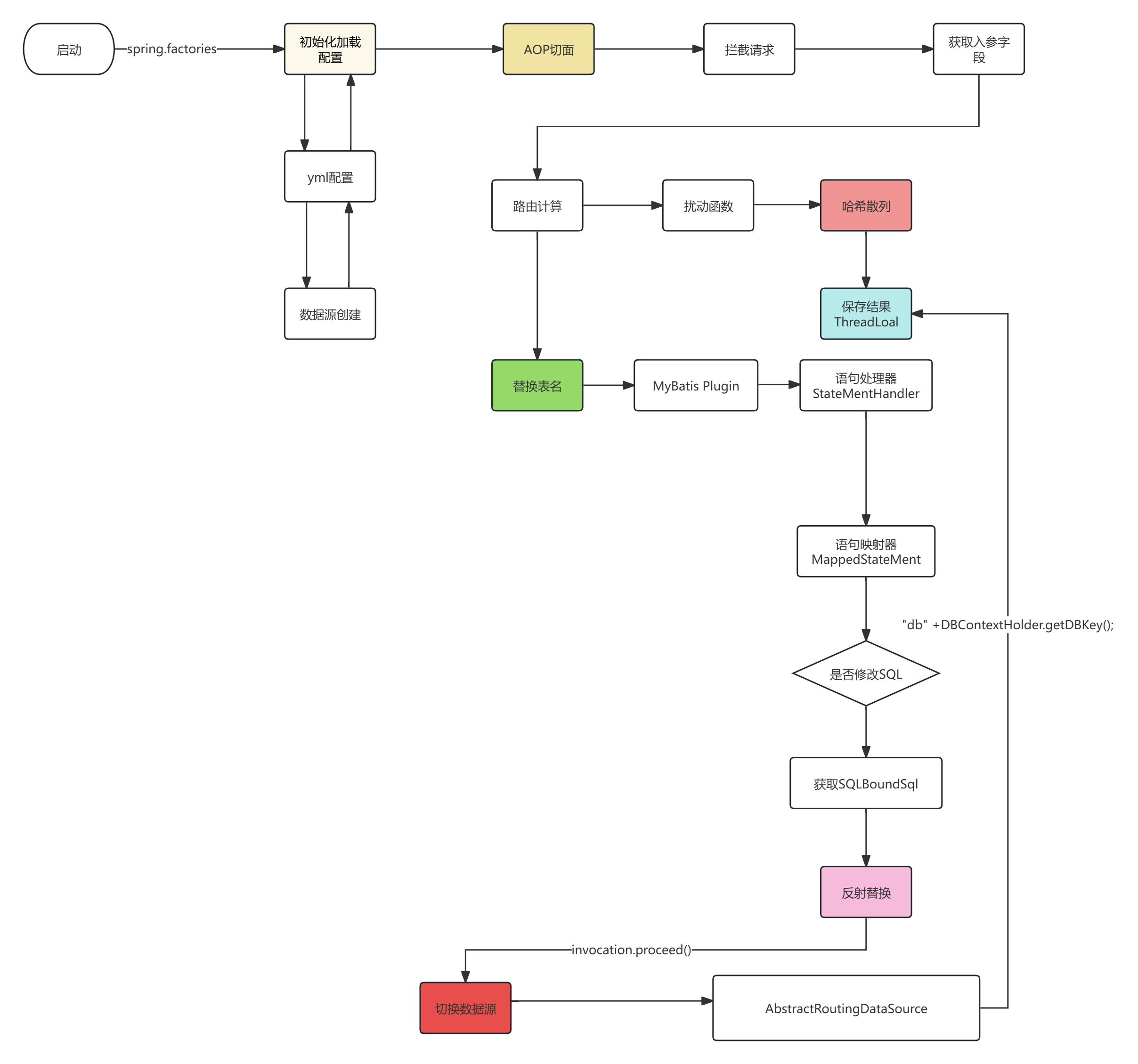
核心代码
切面拦截
在 AOP 的切面拦截中需要完成;数据库路由计算、扰动函数加强散列、计算库表索引、设置到 ThreadLocal 传递数据源,整体案例代码如下:
@Around("aopPoint() && @annotation(dbRouter)")
public Object doRouter(ProceedingJoinPoint jp, DBRouter dbRouter) throws Throwable {
String dbKey = dbRouter.key();
if (StringUtils.isBlank(dbKey)) throw new RuntimeException("annotation DBRouter key is null!");
// 计算路由
String dbKeyAttr = getAttrValue(dbKey, jp.getArgs());
int size = dbRouterConfig.getDbCount() * dbRouterConfig.getTbCount();
// 扰动函数
int idx = (size - 1) & (dbKeyAttr.hashCode() ^ (dbKeyAttr.hashCode() >>> 16));
// 库表索引
int dbIdx = idx / dbRouterConfig.getTbCount() + 1;
int tbIdx = idx - dbRouterConfig.getTbCount() * (dbIdx - 1);
// 设置到 ThreadLocal
DBContextHolder.setDBKey(String.format("%02d", dbIdx));
DBContextHolder.setTBKey(String.format("%02d", tbIdx));
logger.info("数据库路由 method:{} dbIdx:{} tbIdx:{}", getMethod(jp).getName(), dbIdx, tbIdx);
// 返回结果
try {
return jp.proceed();
} finally {
DBContextHolder.clearDBKey();
DBContextHolder.clearTBKey();
}
}
- 简化的核心逻辑实现代码如上,首先我们提取了库表乘积的数量,把它当成 HashMap 一样的长度进行使用。
- 接下来使用和 HashMap 一样的扰动函数逻辑,让数据分散的更加散列。
- 当计算完总长度上的一个索引位置后,还需要把这个位置折算到库表中,看看总体长度的索引因为落到哪个库哪个表。
- 最后是把这个计算的索引信息存放到 ThreadLocal 中,用于传递在方法调用过程中可以提取到索引信息。
Mybatis 拦截器处理分表
- 最开始考虑直接在Mybatis对应的表
INSERT INTO user_strategy_export_${tbIdx} 添加字段的方式处理分表。但这样看上去并不优雅,不过也并不排除这种使用方式,仍然是可以使用的。 - 那么我们可以基于 Mybatis 拦截器进行处理,通过拦截 SQL 语句动态修改添加分表信息,再设置回 Mybatis 执行 SQL 中。
- 此外再完善一些分库分表路由的操作,比如配置默认的分库分表字段以及单字段入参时默认取此字段作为路由字段。
@Intercepts({@Signature(type = StatementHandler.class, method = "prepare", args = {Connection.class, Integer.class})})
public class DynamicMybatisPlugin implements Interceptor {
private Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("(from|into|update)[\\s]{1,}(\\w{1,})", Pattern.CASE_INSENSITIVE);
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// 获取StatementHandler
StatementHandler statementHandler = (StatementHandler) invocation.getTarget();
MetaObject metaObject = MetaObject.forObject(statementHandler, SystemMetaObject.DEFAULT_OBJECT_FACTORY, SystemMetaObject.DEFAULT_OBJECT_WRAPPER_FACTORY, new DefaultReflectorFactory());
MappedStatement mappedStatement = (MappedStatement) metaObject.getValue("delegate.mappedStatement");
// 获取自定义注解判断是否进行分表操作
String id = mappedStatement.getId();
String className = id.substring(0, id.lastIndexOf("."));
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(className);
DBRouterStrategy dbRouterStrategy = clazz.getAnnotation(DBRouterStrategy.class);
if (null == dbRouterStrategy || !dbRouterStrategy.splitTable()){
return invocation.proceed();
}
// 获取SQL
BoundSql boundSql = statementHandler.getBoundSql();
String sql = boundSql.getSql();
// 替换SQL表名 USER 为 USER_03
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(sql);
String tableName = null;
if (matcher.find()) {
tableName = matcher.group().trim();
}
assert null != tableName;
String replaceSql = matcher.replaceAll(tableName + "_" + DBContextHolder.getTBKey());
// 通过反射修改SQL语句
Field field = boundSql.getClass().getDeclaredField("sql");
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(boundSql, replaceSql);
return invocation.proceed();
}
}
- 实现 Interceptor 接口的 intercept 方法,获取StatementHandler、通过自定义注解判断是否进行分表操作、获取SQL并替换SQL表名 USER 为 USER_03、最后通过反射修改SQL语句
- 此处会用到正则表达式拦截出匹配的sql,
(from|into|update)[\\s]{1,}(\\w{1,})
使用
- @DBRouterStrategy(splitTable = true) 配置分表信息,配置后会通过数据库路由组件把sql语句添加上分表字段,比如表 user 修改为 user_003
- @DBRouter(key = "uId") 设置路由字段
- @DBRouter 未配置情况下走默认字段,routerKey: uId
配置分表注解
@Mapper
@DBRouterStrategy(splitTable = true)
public interface IUserStrategyExportDao {
/**
* 新增数据
* @param userStrategyExport 用户策略
*/
@DBRouter(key = "uId")
void insert(UserStrategyExport userStrategyExport);
/**
* 查询数据
* @param uId 用户ID
* @return 用户策略
*/
@DBRouter
UserStrategyExport queryUserStrategyExportByUId(String uId);
}